What is enterprise AI? Why should your business implement enterprise AI??
Enterprise AI defines the strategic application of technologies like machine learning and natural language processing to solve complex business challenges within large organizations. Adoption rates have reached mainstream status because 87% of large enterprises now implement these solutions to maintain a competitive advantage.
These technologies elevate your business performance by automating routine tasks, while productivity increases significantly since your employees can focus on more creative tasks. First, strategic decision-making becomes sharper through data-driven insights. Second, your customer service teams can provide constant support because hyper-personalization improves the user experience.
This article from Groove Technology defines enterprise AI and explains the reasons your business should implement it alongside the specific types available today. The following sections explore the measurable benefits that impact your bottom line as well as the common challenges and key technology considerations required for success. This analysis outlines the specific steps your company must take to implement these tools and provides real-world use cases to illustrate these practical strategies.
1. What is enterprise AI?
Enterprise AI refers to the strategic integration of artificial intelligence technologies, particularly machine learning and natural language processing, into the daily operations of large organizations. By adopting these capabilities, enterprise teams can automate complex workflows, optimize resources, and generate measurable business value across multiple departments.
However, enterprise AI differs significantly from consumer-facing AI applications. Rather than operating in isolation, enterprise systems must integrate seamlessly with existing IT infrastructure while handling large volumes of sensitive data. As a result, robust security protocols, strict governance frameworks, and strong data control mechanisms form the foundation of these platforms, enabling them to scale reliably according to each organization’s specific requirements.
In practice, enterprise AI is no longer an experimental concept but a critical competitive advantage. According to data from Second Talent, 87% of large enterprises have already implemented these solutions. More importantly, most organizations report an average 34% improvement in operational efficiency within just 18 months, driven by process automation and overall performance optimization.

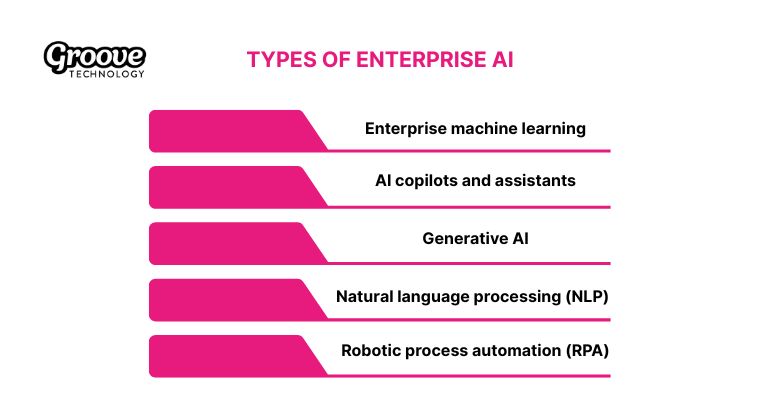
2. Types of enterprise AI
Industry experts divide these powerful technologies into 5 specific categories that serve different operational functions within a company.
- Enterprise machine learning: Foundational algorithms analyze massive datasets to identify hidden patterns and predict future outcomes with high accuracy. Deep learning models in this category power advanced speech recognition systems, while retailers use them to deliver personalized customer experiences.
- AI copilots and assistants: Smart applications act as digital partners for your employees and learn from daily interactions to improve performance. Your teams use them to automate administrative tasks or transcribe meetings, so everyone can focus on creative problem-solving.
- Generative AI: Advanced logic systems use human-like reasoning to assist in the creation of fresh content and complex data models. Designers leverage these tools for rapid product prototyping while marketing teams generate realistic assets for global campaigns.
- Natural language processing (NLP): This underlying capability interprets and generates human language so machines understand your requests without confusion. Chatbots rely on this technology to manage routine customer support queries and allow your human agents to handle high-value conversations.
- Robotic process automation (RPA): Software bots handle repetitive tasks across different systems to streamline your complex operational workflows. HR departments use this technology for data entry and transaction processing because it connects disparate platforms such as ERP and CRM tools.
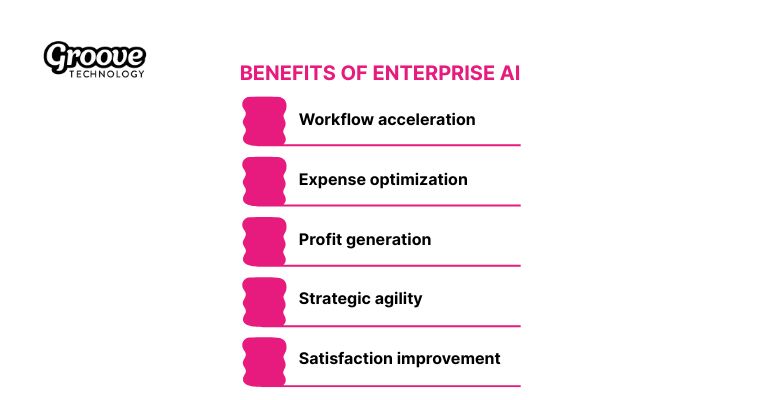
3. Benefits of enterprise AI
Your organization gains measurable value quickly through these 5 distinct benefits that directly impact your bottom line.
- Workflow acceleration: Enterprise AI streamlines time-consuming manual processes that are prone to errors. For example, in supply chain operations, AI systems can automate order reconciliation, forecast demand, and identify potential disruptions earlier than traditional methods. This allows operational teams to focus on higher-value tasks such as supplier optimization and logistics planning.
- Expense optimization: As Brain Raiser stated, organizations achieve an average of 27% cost savings when intelligent inventory management significantly reduces excess stock. In practice, companies like General Mills saved over $20 million by effectively reducing logistics waste through AI-driven forecasting.
- Profit generation: Second Talent mentioned that recommendation engines boost sales by 19% on average since personalization increases customer lifetime value. High-performing firms report 5% growth in earnings before interest and taxes due to rapid scaling.
- Strategic agility: With enterprise AI, decision-makers no longer need to wait for monthly or quarterly reports. Real-time analytics dashboards provide early signals of market trends, demand shifts, or operational risks. This capability is especially valuable in fast-moving industries, where timely responses can determine competitive advantage.
- Satisfaction improvement: Also from Second Talent’s report, hyper-personalized interactions increase customer satisfaction by 24%, while proactive support resolves problems before they escalate. HR departments improve retention rates by automating routine onboarding tasks for new staff members.
4. Challenges of enterprise AI
Complexities often arise during implementation, so we identified 5 major barriers that affect the success rates of growing companies.
- Data integrity issues: According to Teknowledge, poor quality and fragmentation affect 54% of enterprises because reliable models require clean inputs to function correctly. Furthermore, Deloitte reports that legacy systems complicate integration efforts for 60% of leaders, as siloed departments hinder effective training across the organization.
- Expertise gaps: Many organizations lack internal teams that understand both AI and business operations. Overreliance on external vendors makes it difficult to manage models or measure real impact. As a result, AI initiatives often remain stuck at the pilot stage because internal teams cannot scale or optimize the solution after deployment.
- Compliance complexities: Security concerns are blocking scaling efforts for many companies, and per Netser Group, cybersecurity remains the top worry for 48% of decision-makers.Most firms lack established frameworks despite high prioritization, since regulatory fragmentation exposes organizations to serious ethical privacy breaches.
- Scalability roadblocks: While AI pilots may succeed in isolated environments, expanding them across the enterprise is challenging. The main obstacles are unclear business value, rising operational costs, and misaligned processes. A demand forecasting model that works well in one region, for example, may fail at scale due to differences in data quality and workflows.
- Cultural resistance: Legacy infrastructure is a significant hurdle; Netser Group highlights that it limits 93% of CIOs because outdated tech stacks cannot support modern algorithmic requirements or real-time processing needs. Internal resistance creates significant adoption drag since organizational silos and fear of change complicate enterprise-wide rollout.
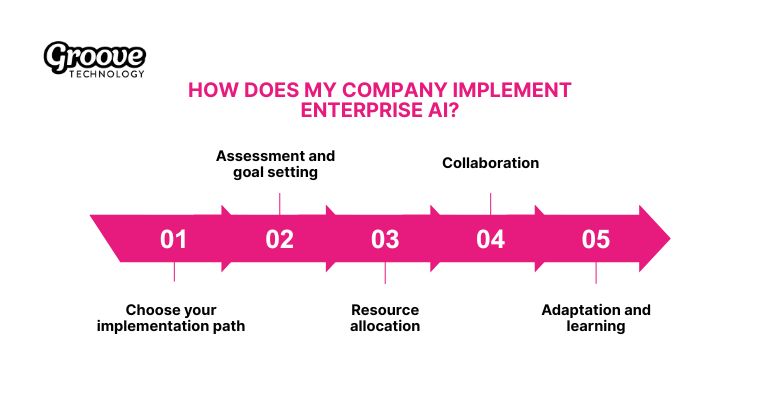
5. How does my company implement enterprise AI?
To unlock real value from AI, organizations must take a structured, business-driven approach rather than treating it as a standalone technology project. Below are five practical steps to help companies implement enterprise AI effectively and sustainably.
- Step 1 – Choose your implementation path: At the outset, leadership must make a foundational decision: build AI capabilities in-house or partner with external experts. This choice affects not only cost and deployment speed, but also the future scalability and flexibility of your technology stack.
- In-house implementation: This approach works best for organizations with strong technical teams. Building internally provides full control over systems, ensures data confidentiality, and allows for tailored solutions. However, it often comes with a steeper learning curve and greater demands on internal resources.
- Partner implementation: Working with experienced vendors accelerates deployment and provides immediate access to proven expertise. While this reduces skill-related risks, success depends on selecting a partner whose capabilities, values, and operating model align with your organization.
- Step 2 – Assessment and goal setting: AI initiatives succeed only when guided by well-defined goals. Organizations should establish measurable objectives that directly support business priorities such as operational efficiency, cost reduction, or customer experience. At the same time, a thorough data assessment is essential to evaluate data quality, security, and readiness before technical implementation begins.
- Step 3 – Resource allocation: Enterprise AI requires more than upfront technology investment. Companies must plan for ongoing costs related to system maintenance, model updates, and cybersecurity. Equally important is human capital. Whether through hiring specialists or upskilling existing teams, investing in people ensures that AI tools are used effectively and deliver meaningful returns.
- Step 4 – Collaboration: Because AI impacts multiple functions, early and continuous collaboration between IT teams, business units, and leadership is critical. Regular progress reviews help teams stay aligned with strategic objectives and allow for timely adjustments. This collaborative approach minimizes risk while increasing organizational buy-in.
- Step 5 – Adaptation and learning: Enterprise AI is an ongoing journey, not a one-off deployment. As technology evolves and business needs shift, organizations must continuously refine their systems and strategies. Ongoing training builds employee confidence, while structured feedback loops ensure AI solutions remain relevant, reliable, and aligned with real-world use cases.
6. Enterprise AI use cases
Leading global companies currently apply this technology in 5 specific ways to solve real problems and generate value.
- Operations and supply chain: Siemens and Walmart use predictive algorithms to forecast machinery failures and demand shifts accurately. These systems improve logistics fleets and minimize downtime by analyzing vibration data and historical sales patterns.
- Marketing and sales: Brands like Coca-Cola use generative tools to quickly create thousands of ad variations. Salesforce Einstein is an automated assistant that drafts emails, allowing sales teams to focus on closing deals.
- Finance and risk management: JPMorgan Chase employs machine learning to analyze millions of transactions and detect fraud in real time. Financial institutions run economic simulations that stress-test portfolios against market crashes to protect assets effectively.
- Human resources: Companies like Eaton use algorithms to parse resumes and match skills without demographic bias. IBM uses internal chatbots to answer routine benefit questions so HR staff can handle complex employee relations issues.
- IT and software development: Developers use GitHub Copilot to generate boilerplate code and write unit tests 55% faster. AIOps systems monitor server health to detect anomalies and reroute traffic before human engineers notice problems.

7. What are the key technology considerations when applying enterprise AI?
Successful deployment requires your organization to implement these 5 fundamental architectural components effectively.
- Data management: Data engineering pipelines provide secure access to your assets, while centralized catalogs enable scientists to find information quickly. Governance mechanisms regulate this access and support risk management efforts without creating unnecessary obstacles for your teams.
- Model training infrastructure: A centralized infrastructure supports the development of new models, as feature stores enable different teams to collaborate without duplicating work. RAG systems adapt existing algorithms with your internal knowledge base so you avoid the cost of retraining massive models.
- Central model registry: This enterprise catalog tracks version history and enables your developers to compare performance across iterations efficiently. Detailed metadata records enhance collaboration among business units and streamline compliance for every deployed asset.
- Model deployment: MLOps practices improve operational efficiency by applying proven DevOps principles to the unique challenges of machine learning. Automated pipelines facilitate continuous integration and allow your teams to update models rapidly based on real-time feedback.
- Model monitoring: Continuous oversight ensures reliability, as algorithms occasionally produce inaccurate information or hallucinations during interactions. Domain experts must assess outputs periodically to maintain integrity and verify that the system meets the evolving needs of your stakeholders.
This article defined enterprise AI and outlined the strategic roadmap for successful implementation within your business. We analyzed specific types, proven benefits, and potential challenges to help you make informed adoption decisions. You now have the insights needed to select the right tools and drive real operational value.
Groove Technology acts as your strategic partner for technical excellence and sustainable growth. Since 2016, our high-performance teams in Vietnam have delivered tailored software to clients globally. Connect with us to build your AI and Machine Learning solutions, AI Outsourcing Solutions, AI Agent Solutions, or AI Data Analytics Solutions.





