What is AI Analytics? A Comprehensive Guide 2026
AI analytics leverages artificial intelligence and machine learning to automate complex data processing, transforming raw information into actionable insights far faster than traditional manual methods. By identifying patterns at scale, this approach allows your team to move beyond simple data collection toward high-speed, data-driven decision-making.
Unlike traditional analytics, which often force a reliance on static dashboards and slow reporting cycles, AI analytics proactively surfaces insights and delivers real-time alerts. The workflow typically begins with defining a problem and establishing a clean data foundation; from there, it utilizes descriptive and diagnostic modeling to explain past events, while simultaneously applying predictive and prescriptive analytics to forecast future trends and recommend specific strategic actions.
By integrating advanced technologies like natural language processing and neural networks, AI-powered analytics systems can effectively uncover hidden trends and handle unstructured data. This article from Groove Technology explores how these components work together, outlining the specific benefits and challenges your business may encounter when building a robust, AI-driven data advantage.

1. What is AI analytics?
AI analytics is the application of machine learning and natural language processing into data analytics so you can automatically process massive, complex datasets. This approach turns raw information into clear answers because the algorithms identify patterns and predict specific trends.
Your team gains a distinctive advantage with AI-powered business analytics, as the software detects anomalies and provides recommendations faster than standard manual methods allow. Computers handle the heavy data mining so you focus on the decisions that actually drive business value.

2. AI-Powered Analytics vs. Traditional Data Analytics
AI-powered data analytics stands apart from traditional data methods through its superior processing speed, automation capabilities, and the depth of insights it delivers. Traditional methods rely heavily on manual workflows where technical teams must extract data and build static dashboards to generate periodic reports. Consequently, businesses often face delays, limited flexibility, and slower response times due to human bottlenecks.
In contrast, AI-powered analytics operate in a continuous and automated manner, flipping the old model by processing massive datasets in real time. Powered by machine learning and deep learning, the system detects anomalies the moment they occur and surfaces patterns without the need for manual hunting. This allows the software to move beyond merely explaining what happened to predicting what will occur next and recommending specific actions.
In essence, while traditional analytics is descriptive and reactive, AI analytics is proactive, predictive, and action-oriented. This shift empowers organizations to move from waiting for data to making immediate, highly dynamic decisions. The comparison below highlights the fundamental functional differences between these two approaches:
| Traditional Analytics | AI-Powered Analytics |
| Static dashboards needing constant updates | Dynamic insights that adjust in real-time |
| Manual reports built by technical teams | Instant answers without waiting on analysts |
| Descriptive views showing what happened | Predictive guidance showing what happens next |
| High learning curve for non-technical users | Conversational interfaces designed for everyone |
| Siloed tools and fragmented workflows | Embedded insights integrated across applications |
| Limited scalability for big data sets | Architecture built for high volume and velocity |
3. How AI-Powered Analytics Works?
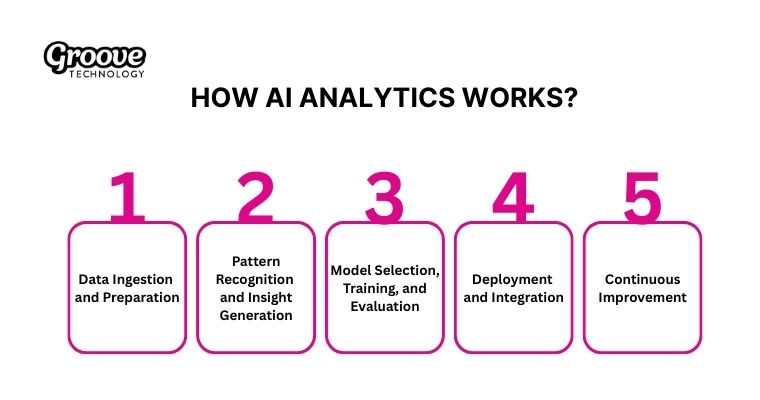
AI-Powered data analytics operates through a clear 5 steps workflow, with each stage playing a crucial role in generating accurate, actionable insights.
- Step 01 – Data Ingestion and Preparation: The process begins when you collect raw data from various databases and APIs while the system simultaneously cleans the records to remove errors. This preparation stage standardizes your formats and restructures the information so that your models receive high-quality inputs for the next stages of analysis.
- Step 02 – Pattern Recognition and Insight Generation: Once the data is prepared, algorithms scan and analyze it to uncover hidden correlations and anomalies that human analysts often overlook. Machine learning models automatically extract features from these datasets, enabling clear diagnostic and predictive insights for your team.
- Step 03 – Model Selection, Training, and Evaluation: Based on your project goals, data scientists select appropriate model architectures such as decision trees or neural networks. These models are then trained using labeled datasets and evaluated through rigorous metrics to ensure accuracy before moving into real-world deployment.
- Step 04 – Deployment and Integration: After the model reaches the desired performance threshold, developers deploy it into production environments using cloud platforms or efficient APIs. This integration connects insights directly to your operational workflows, allowing real-time dashboards to trigger immediate actions such as dynamic pricing updates or fraud alerts.
- Step 05 – Continuous Improvement: Monitoring systems track your model performance continuously to detect any data drift or unexpected declines in accuracy as your business environment changes. Feedback loops initiate automated retraining cycles with updated information so that your analytics remain reliable and relevant even when market conditions or user behaviors shift unexpectedly.
4. Types of AI analytics
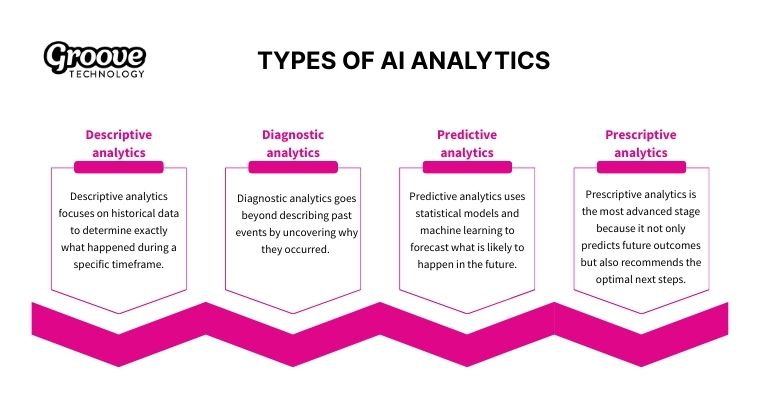
Modern data strategies typically utilize four distinct categories of analysis to transform raw information into decision-making power.
4.1. Descriptive analytics
Descriptive analytics explains exactly what happened in your data.
Descriptive analytics focuses on historical data to determine exactly what happened during a specific timeframe. It forms the foundation for deeper analysis because it provides a clear baseline before exploring root causes or enabling AI-powered predictive analytics to forecast future outcomes. By aggregating metrics such as total revenue, website traffic, or campaign performance, descriptive analytics helps teams understand the big picture.
Typically, visual dashboards display these metrics so teams can quickly assess the current state of the business. However, AI enhances this process by generating natural language summaries and automatically detecting patterns without manual queries. Tools like Tableau exemplify this ability by transforming complex datasets into easy-to-read visualizations.
4.2. Diagnostic analytics
Diagnostic analytics reveals why it happened by identifying root causes.
Diagnostic analytics goes beyond describing past events by uncovering why they occurred. This approach uses root cause analysis and correlation mapping to identify the underlying factors that drive specific outcomes. Within AI-powered reporting and analytics platforms, these diagnostic capabilities help transform descriptive reports into deeper insights that explain performance changes.
Algorithms dig deeper into descriptive outputs to identify hidden contributors—such as the main drivers behind customer churn, sudden revenue declines, or unusual behavioral changes. Platforms like SAS Visual Analytics excel in this area by detecting relationships that human analysts might overlook during manual review. As a result, you gain insight into the context behind the numbers, rather than simply observing the final outcome.
4.3. Predictive analytics
Predictive analytics forecasts what is likely to happen next based on historical patterns.
Predictive analytics uses statistical models and machine learning to forecast what is likely to happen in the future. By analyzing patterns in historical data, predictive models estimate probabilities related to events such as sales growth, fraud risks, demand fluctuations, or operational performance. This forward-looking capability empowers businesses to act proactively rather than merely reacting to changes.
AI accelerates the forecasting process with tools like Power BI, which now includes rapid anomaly detection and scenario simulation features. Marketing teams rely on AI-powered predictive analytics to plan strategies, anticipate customer behavior, and prepare for market shifts before they occur. Predictive analytics provides a future-oriented perspective instead of simply reviewing the past.
4.4. Prescriptive analytics
Prescriptive analytics recommends what you should do next using optimization and scenario modeling.
Prescriptive analytics is the most advanced stage because it not only predicts future outcomes but also recommends the optimal next steps. By combining complex predictions with optimization algorithms, it guides decision-makers on exactly what actions to take to achieve the best possible results. This is especially valuable for strategic areas such as pricing adjustments, resource allocation, and supply chain optimization.
Generative models and scenario simulations test multiple options to determine the optimal strategy based on your unique constraints and business goals. Platforms like ThoughtSpot leverage these capabilities to deliver automated alerts and real-time recommendations across the enterprise. As a result, you receive a concrete action plan, not just a list of potential possibilities.
5. The four key elements of AI analytics
Successful AI systems rely on these 4 distinct technical components to process information effectively.
- Natural language processing (NLP): Natural language processing enables computers to interpret human speech and text accurately. This technology scans unstructured content like emails because it identifies sentiment and specific themes automatically. Example: A support system uses NLP to route tickets based on the customer’s emotional tone.
- Machine learning (ML): Machine learning algorithms train models to recognize patterns without rigid programming rules. Within AI-powered analytics consulting engagements, this capability is used to help organizations predict outcomes as models learn from historical data and improve continuously with new inputs. Example: Streaming services use machine learning to recommend movies based on your viewing habits.
- Neural networks: Neural networks mimic biological brain structures through layers of interconnected data nodes. These systems solve complex classification problems because they process information non-linearly to find relationships standard tools miss. Example: Financial institutions apply neural networks to flag suspicious activity across millions of accounts instantly.
- Deep learning: Deep learning utilizes multiple network layers to analyze massive amounts of unstructured information. This method handles complex inputs like images or audio files without needing manual guidance from data scientists. Example: Medical software uses deep learning to detect anomalies in X-rays with high precision.

6. Benefits of AI-Powered analytics
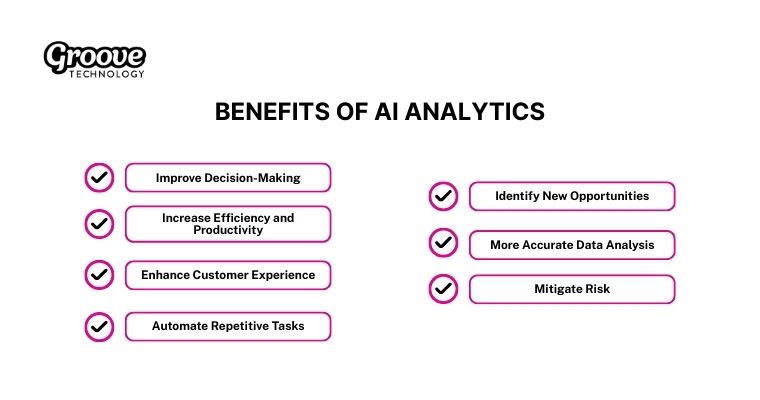
Organizations gain these 7 distinct advantages when they integrate intelligent AI powered data analytics solutions into their data strategy.
- More Accurate Data Analysis: AI algorithms analyze massive datasets efficiently so you do not need constant manual review. This technology identifies complex patterns that humans often miss during standard checks.
- Improve Decision-Making: Predictive models process historical records to provide clear recommendations for your future strategy. Business leaders use these insights to make choices that drive real growth.
- Automate Repetitive Tasks: Automation tools handle boring data entry and processing tasks so your analysts focus on strategy. This shift reduces human error because machines perform consistent calculations every time.
- Increase Efficiency and Productivity: Smart workflows accelerate data processing speeds so your team derives value immediately. Efficiency gains translate into direct cost savings because you allocate resources more effectively.
- Enhance Customer Experience: Analytical tools examine user behavior to help you personalize marketing campaigns and support interactions. Your customers feel valued since the service adapts to their specific needs.
- Identify New Opportunities: An ai powered analytics product scans market trends to reveal potential growth areas that traditional methods usually overlook. Companies use this information to innovate products and capture new segments early.
- Mitigate Risk: Security models detect data anomalies in real-time to warn you about potential threats. Your team takes preventive measures instantly so the business avoids costly disruptions.
7. Challenges of AI-Powered Analytics
Business leaders often encounter 4 distinct hurdles when they attempt to integrate these advanced systems into their existing workflows.
- Initial Costs and Startup Time: The investment demands heavy upfront capital for hardware and data experts before you see real value. Your company must build complex data flows before the software delivers any actionable insights.
- Statistical Selection Bias: Unsupervised models inherit the prejudices hidden inside your training data and produce skewed results. These algorithms reflect the flaws of the input information because they lack human nuance and context.
- Technical Expertise: Your team requires specialized skills to configure these advanced tools and evaluate the outputs effectively. Many organizations struggle to recruit the expensive data scientists needed to maintain these sophisticated workflows.
- Transparency: AI systems frequently operate as black boxes that hide the logic behind their specific decisions. Stakeholders often find it difficult to trust the results without clear explainability regarding the process.
8. Practical use cases of AI-Powered Analytics
Diverse sectors now rely on these intelligent tools to solve complex problems, so here are 8 distinct industries that benefit directly:
- Energy and Utilities: Utility companies analyze equipment logs because the system predicts future energy demand accurately based on consumption patterns from previous years’ data.
- Financial Services: Financial institutions apply these tools so they can predict loan defaults and detect fraud patterns before money actually leaves the bank.
- Healthcare: Healthcare networks employ forecasting tools so administrators anticipate patient admission rates and manage critical resources effectively during those busy seasons.
- Insurance: Insurance providers deploy analytical models because the software assesses application risks and predicts the likelihood of future claims accurately for every policyholder.
- Life Sciences: Research groups develop patient personas so the scientists can estimate the probability of non-adherence to specific treatment plans early on.
- Manufacturing and Supply Chain: Supply chain managers forecast inventory needs because the analytics identify hidden factors that frequently lead to expensive production failures and delays.
- Public Sector: Government agencies analyze population trends so planners make informed decisions regarding infrastructure investments and future public works projects for the community.
- Retail and CPG: Retail brands study historical data because the algorithms determine which specific promotional offers will drive the highest sales volume next quarter.

9. Ethical Considerations of AI-Powered analytics
Implementing these powerful tools requires a strong moral compass, so you must address these 4 critical ethical considerations.
- Bias and Fairness: Skewed training data often amplifies existing prejudices because the algorithms unknowingly replicate historical discrimination against specific groups. Your team must implement rigorous audits and diverse datasets so the software provides equitable outcomes for every user.
- Privacy and Consent: Data collection practices require strict adherence to regulations like GDPR because personal information demands protection against unauthorized surveillance. Anonymization techniques secure individual identities while the system processes the necessary analytics for your business goals.
- Transparency and Explainability: Black box models frequently obscure the decision-making process since complex algorithms are difficult for non-technical stakeholders to interpret. Clear documentation builds trust because users need to understand exactly how the system reached a specific conclusion.
- Accountability and Manipulation: Organizations must establish clear oversight protocols because unchecked automation sometimes leads to manipulation or harmful errors. Governance frameworks ensure that human supervisors remain responsible for the actions and decisions generated by artificial intelligence.

10. History of AI-Powered analytics
The history of AI analytics traces the evolution of technology through these 5 significant milestones.
- Early foundations (1950s-1960s): Alan Turing established the theoretical groundwork because his research defined the initial concepts of computing and intelligence. Researchers focused on rule-based systems during this era since these precursors laid the path for modern analytical techniques.
- Growth of machine learning (1970s-1980s): Statistical methods transformed artificial intelligence so systems could actually learn from data instead of just following rules. Neural networks emerged during this period as expert systems began to handle more complex reasoning tasks for researchers.
- Data explosion and early AI tools (1990s): The internet created a massive surge in digital information because global connectivity generated data at unprecedented speeds. Analytical tools integrated directly with warehousing systems since businesses needed to organize this sudden influx of raw records.
- Advancements in algorithms and big data (2000s): Computing power increased dramatically so developers built sophisticated models capable of processing “big data” effectively. Advanced solutions became necessary because standard methods failed to handle the volume and variety of these massive datasets.
- Deep learning and modern AI analytics (2010s-Present): Deep learning revolutionized the field because multi-layered neural networks now power advanced applications like computer vision. Cloud computing integrates these capabilities across industries since modern platforms process natural language and IoT data in real-time.
11. Future of AI-Powered Analytics
The industry is currently shifting toward 3 major trends that will define how your business handles data in the coming years.
- Augmented Analytics: Augmented analytics uses machine learning to automate data preparation and insight generation for your team. This technology allows non-technical staff to ask plain questions and receive clear answers without needing help from a data scientist.
- Real-Time and Edge Analytics: Edge computing processes information directly at the source instead of sending everything to a central cloud server. This method reduces latency significantly because factory sensors and medical devices need to make split-second decisions locally.
- Autonomous AI Agents: Autonomous agents execute specific tasks and make independent decisions based on the goals you set for them. These systems solve problems proactively across your workflows rather than just waiting for a human to review the reports.
This guide defines the mechanics and benefits of AI-powered analytics so you understand how the technology works. You can now move beyond static dashboards because the sections on predictive models and future trends clarified the path to proactive decisions.
Groove Technology builds high-performance software teams to support clients across Australia and Europe. We act as your strategic partner since we deliver custom solutions that align directly with your business goals.
Our experts specialize in AI and Machine Learning as well as AI Solutions Outsourcing. Your company gains technical excellence through our specific AI Agent Solutions and AI Data Analytics Solutions.





